💢Historical purposes only
💢Proud member of the U.S. Military! 🇺🇸
💢Kik-Marcell824
💢#KeepHistoryAlive
💢Colored photos belong to their respective owners
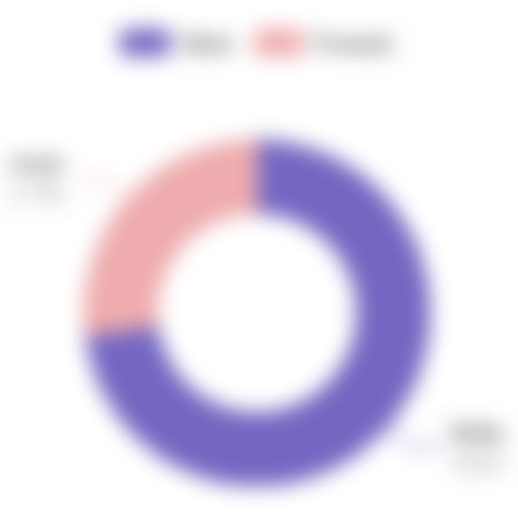
6% @the_history_of_ww2 jälgijatest on naised ja 94% on mehed. Postituste keskmine kaasatusmäär on umbes 1.28%. Keskmiselt saab iga postitus 1,587 meeldimist ja keskmiselt on 12 kommentaari.
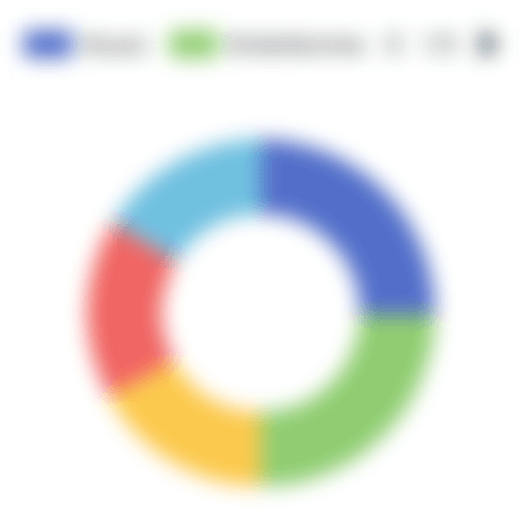
@the_history_of_ww2 armastab postitada teemadelHaridus,
Kodu ja aed,
Guns。
124,970
Jälgijad
1.28%
Kaasamise määr

1,599
Kaasamine postituse kohta
1,587
Keskmine meeldimised postituse kohta
12
Keskmine kommentaarid postituse kohta

104,125
Üleilmne edetabel
52,689
Riigi edetabel
-
Kategooria edetabel
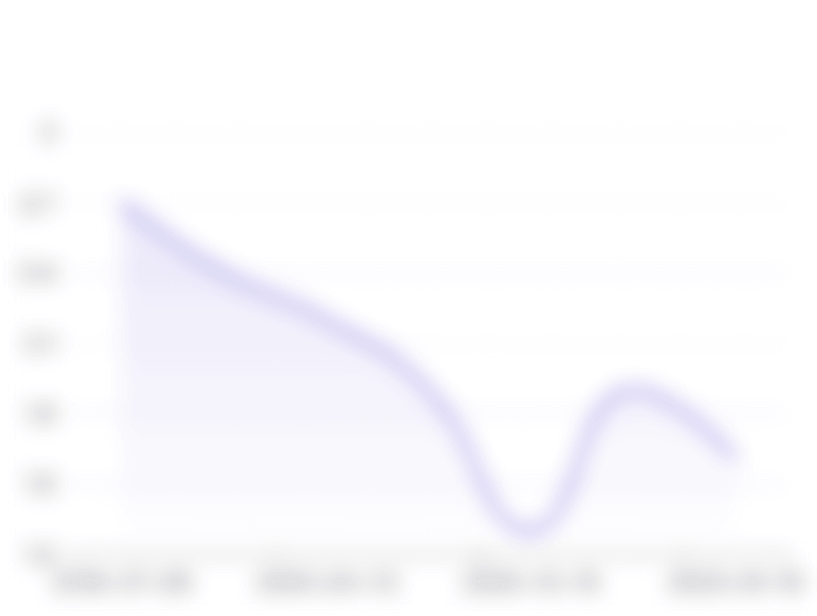
Jälgijate ja postituste kasvutrend
Kaasatuse Määra Kasvutrendid
Kaasamise määr
Meeldimised ja kommentaarid
Märkimisväärsed mõjutajad
Auditooriumi brändieelistused
Sarnased kontod

Hiljutised postitused
* Autoriõigus: Sisu loojad on vaikimisi autorikaitse õiguste omanikud. Need teave, sealhulgas pildid, tekstid, videod, postitused ja profiilid, on avaldatud avalikel domeenidel ja vastavatel sotsiaalmeedia platvormidel avaliku vaatamise eesmärgil.
KKK: Instagram statistika ja teadmiste hankimine @the_history_of_ww2
Kuidas saan Instagram statistikat ja analüütikat @the_history_of_ww2 kohta hankida?
StarNgage pakub põhjalikke analüütilisi aruandeid, mis annavad olulisi kriteeriume ja teadmisi, et saaksite @the_history_of_ww2 kohta täieliku ülevaate. Saate uurida erinevaid aspekte, sealhulgas Instagram jälgija statistikat, nagu jälgija ja postituste kasvu tendentsid, kaasamise määr ja selle kasvutrendid. Lisaks saate teavet keskmise meeldimiste ja kommentaaride arvu kohta postituse kohta, teavet jälgija demograafia kohta, brändisidususe andmeid, oluliste räsimärkide mainimisi, sarnaseid kontosid ja viimaseid postitusi.
Mis on hetke jälgijate arv @the_history_of_ww2 kohta Instagram?
Kuni viimase uuenduseni on @the_history_of_ww2 kogunud pühendunud jälgijaskonna koos 124,970 jälgijaga Instagram.
Millised teadmised ja analüütilised andmed sisalduvad täielikus aruandes @the_history_of_ww2 kohta Instagram?
Meie täielik Instagram analüütiline aruanne annab põhjaliku ülevaate @the_history_of_ww2 kohta Instagram. See aruanne sisaldab üksikasjalikku teavet ajas kasvava jälgijate arvu, kaasamismõõdikute ja postituste sageduse kohta nii nädalas kui ka kuus. Selle põhjaliku aruande saamiseks palun registreeruge ja looge uus StarNgage konto või logige sisse oma olemasolevasse kontosse.
Kas ma saan jälgida, kuidas on muutunud @the_history_of_ww2 kaasamismäär Instagram?
Jah, StarNgage analüütikavahendid võimaldavad teil jälgida @the_history_of_ww2 kaasamismäära ajas Instagram. See teave aitab teil hinnata @the_history_of_ww2 kaasamisstrateegiate tõhusust.
Kuidas mõjutab @the_history_of_ww2 jälgijate demograafia teadmine Instagram?
@the_history_of_ww2 jälgijaskonna demograafilise teabe mõistmine Instagram on äärmiselt väärtuslik. See võimaldab teil kohandada oma mõjujõu sisu ja turundusstrateegiaid, et need oleksid paremini kooskõlas @the_history_of_ww2 jälgijatega, kuna teil on teavet nende vanuse, soo, asukoha ja huvide kohta.
Kuidas saan kasutada brändisidususe andmeid oma turundusstrateegia parandamiseks Instagram koos @the_history_of_ww2?
Brändisidususe andmed on võimas tööriist, mis aitab teil mõista, millised brändid või tooted teie sihtrühm kõige rohkem huvitavad. See teave aitab teil oma sisu koostööd ja partnerlussuhteid täiustada Instagram, suurendades seeläbi kaasamist teie sihtgrupiga.