Naturopathic Doctor 🌿
Vegan 🌱
Athlete ⚽️
Clinic: @tonumeintegratedhealth 🏥
Posts are for educational purposes only and are not medical advice 🚫
نسبة -% من متابعي @dr.matthewnagra لديهم نسبة أنثى، و -% ذكور. معدل التفاعل المتوسط على المنشورات حوالي 1.7%. المتوسط لعدد الإعجابات في الردود هو 564 وعدد الإعجابات في المتوسط هو 34.
@dr.matthewnagra يحب نشر حولاللياقة البدنية والصحة.
34,616
المتابعون
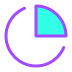
1.7%
معدل المشاركة

598
المشاركة لكل منشور
564
متوسط الإعجابات لكل منشور
34
متوسط التعليقات لكل منشور

225,844
الترتيب العالمي
17,856
ترتيب البلد
-
ترتيب الفئة
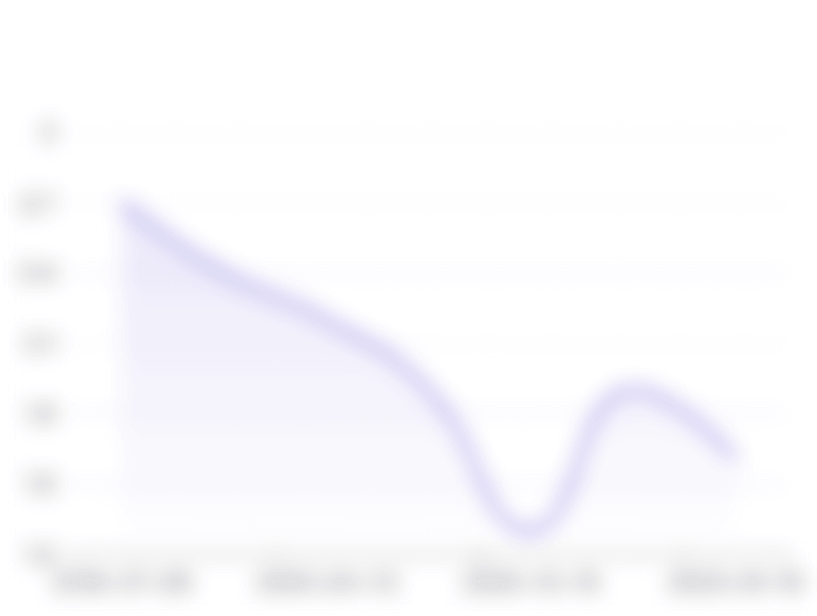
اتجاهات نمو المتابعين والمنشورات
اتجاهات نمو معدل المشاركة
جنس الجمهور

مجموعة العمر المهيمنة
الاهتمامات

الإشارات - الحسابات
معدل المشاركة
الإعجابات والتعليقات
المؤثرين الملفتين للانتباه
قبول الجمهور للعلامة التجارية
الحسابات المماثلة













المنشورات الأخيرة
* حقوق النشر: صانعو المحتوى هم أصحاب حقوق النشر الافتراضيين. يتم نشر هذه المعلومات بما في ذلك الصور والنصوص ومقاطع الفيديو والمنشورات والملفات الشخصية على المجالات العامة ووسائل التواصل الاجتماعي المقابلة للمشاهدة العامة.
الأسئلة الشائعة: إحصائيات ورؤى Instagram لـ @dr.matthewnagra
كيف يمكنني الوصول إلى إحصائيات وتحليلات Instagram لـ @dr.matthewnagra؟
يوفر StarNgage تقارير تحليلية شاملة تقدم مؤشرات رئيسية وإضافات لتمنحك فهمًا كاملاً لـ @dr.matthewnagra. يمكنك استكشاف جوانب مختلفة بما في ذلك إحصائيات المتابعين في Instagram مثل اتجاهات نمو المتابعين والمنشورات ومعدل المشاركة واتجاهاتها. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يمكنك الوصول إلى معلومات عن المتوسط لعدد الإعجابات والتعليقات في المنشور الواحد وإلمام بإحصاءات الجمهور أو ديموغرافيته، وبيانات الالتزام بالعلامة التجارية، والإشارات إلى وسم ذي صلة، والحسابات المماثلة، وآخر المنشورات.
ما هو عدد المتابعين الحالي لـ @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram؟
حتى آخر تحديث، حصل @dr.matthewnagra على متابعين مخلصين مجموعهم 34,616 متابع في Instagram.
ما هي الإضافات والتحليلات التي تشتمل عليها التقارير الكاملة لـ @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram؟
تحتوي تقريرنا التحليلي الكامل لـ Instagram على نظرة شاملة لـ @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram. يتضمن هذا التقرير معلومات تفصيلية حول نمو المتابعين مع مرور الوقت، ومعدلات المشاركة، وتواتر المنشورات، سواء على أساس أسبوعي أو شهري. للوصول إلى هذا التقرير المفصل، يرجى التسجيل وإنشاء حساب جديد في StarNgage أو تسجيل الدخول إلى حسابك الحالي.
هل يمكنني تتبع كيف تطور معدل المشاركة لـ @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram؟
نعم، تتيح أدوات التحليل التابعة لـ StarNgage لك تتبع كيفية تطور معدل المشاركة لـ @dr.matthewnagra على مدار الوقت على Instagram. تساعدك هذه البيانات على تقييم فعالية استراتيجيات المشاركة لـ @dr.matthewnagra.
كيف يمكنني فهم ديموغرافي جمهور @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram؟
تجلب فهم ديموغرافي جمهور @dr.matthewnagra على Instagram قيمة كبيرة. يتيح لك ضبط المحتوى الخاص بك واستراتيجيات التسويق مع المؤثرين للتوافق أكثر مع متابعي @dr.matthewnagra، حيث ستحصل على معلومات حول سنهم وجنسهم وموقعهم واهتماماتهم.
كيف يمكنني الاستفادة من بيانات الأفليات العلامة التجارية لتحسين استراتيجيتي التسويق على Instagram مع @dr.matthewnagra؟
تعد بيانات الالتزام بالعلامة التجارية أداة قوية لفهم العلامات التجارية أو المنتجات التي يهتم بها جمهورك. يمكن أن توجهك هذه المعلومات في تعاونك في المحتوى والشراكات على Instagram، مما يعزز الالتزام مع جمهورك المستهدف.